Best Ways To Relieve Fatty Liver Disease – Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Fatty liver disease, or hepatic steatosis, is a condition characterized by excess fat accumulation in the liver. This condition can lead to inflammation and, in severe cases, liver damage. It affects a large number of people worldwide, especially those with obesity, diabetes, or unhealthy lifestyles.
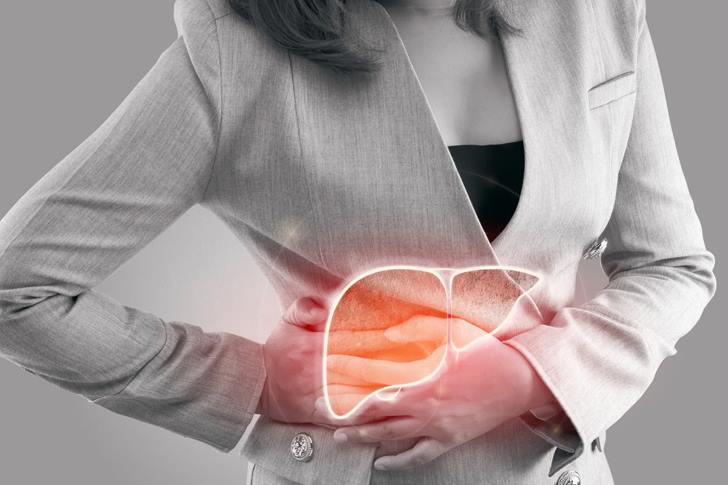

What is Fatty Liver Disease?
Fatty liver disease can be categorized into two types:
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): This occurs in people who drink little or no alcohol. It is primarily linked to obesity, insulin resistance, and poor diet.
- Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD): This occurs due to excessive alcohol consumption, which affects the liver’s ability to break down fats.
Both types of fatty liver disease can progress to more severe conditions like cirrhosis or liver failure if left untreated.
Causes of Fatty Liver Disease
Understanding the root causes of fatty liver disease is the first step toward finding effective treatments. Some common causes include:
- Obesity: Excess fat in the body is stored in the liver, leading to fatty liver.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Insulin resistance can result in fat buildup in the liver.
- High Cholesterol and Triglycerides: Unhealthy fat levels in the blood contribute to liver fat accumulation.
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive drinking damages liver cells, leading to fat buildup.
- Malnutrition: Lack of proper nutrients, especially protein, can impair liver function.
- Genetic Factors: Family history of liver disease can increase the risk.
Symptoms of Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease often develops silently, but as the condition progresses, some symptoms may become noticeable, including:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Discomfort or pain in the upper right abdomen
- Unexplained weight loss
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes)
- Swelling in the legs and abdomen
- Confusion or difficulty concentrating (in severe cases)
Best Ways to Relieve Fatty Liver Disease
Addressing fatty liver disease early can prevent it from progressing into more serious conditions. Here are some of the best ways to relieve and manage this condition:
1. Weight Loss
- Losing 7-10% of body weight has been shown to significantly reduce liver fat and inflammation.
- Regular exercise and a balanced diet can lead to sustainable weight loss.
2. Healthy Diet
- Low-sugar and low-fat foods: Avoid sugary snacks and fried foods. Opt for vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Increase fiber intake: Fiber helps reduce fat absorption. Include fruits, vegetables, and legumes in your diet.
- Limit alcohol: Reduce alcohol consumption to prevent further liver damage.
3. Exercise Regularly
- Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week, including aerobic activities like walking or swimming.
- Strength training can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce fat.
4. Medications
- Some medications, like vitamin E and insulin-sensitizing drugs, can help reduce liver fat and inflammation.
- Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any medication.
5. Manage Underlying Conditions
- Control diabetes: Maintain blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
- Lower cholesterol: Medications and lifestyle changes can help reduce high cholesterol and triglycerides.
6. Liver-Friendly Supplements
- Milk thistle: Contains silymarin, which has anti-inflammatory properties that can protect liver cells.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fish oil, these fats help reduce liver fat and improve liver function.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Fatty Liver Disease
Preventing fatty liver disease requires long-term lifestyle changes. Here are some habits that can protect your liver health:
- Balanced Diet: Incorporate foods rich in antioxidants and avoid processed foods.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to flush out toxins and support liver function.
- Regular Medical Checkups: Get your liver function tested regularly, especially if you have risk factors such as obesity or diabetes.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking exacerbates liver damage and worsens fatty liver disease.
Table: Comparison of Common Fatty Liver Treatments
| Treatment Method | Effectiveness | Cost | Duration | Side Effects | Ease of Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight Loss | High | Low | Long-term | Minimal (with healthy practices) | Moderate |
| Low-fat Diet | High | Low | Ongoing | None (if balanced) | Easy |
| Regular Exercise | High | Low | Long-term | None (with proper technique) | Moderate |
| Vitamin E | Moderate | Medium | Variable | Fatigue, diarrhea | Easy |
| Insulin-sensitizing Drugs | Moderate | High | Ongoing | Hypoglycemia, weight gain | Moderate |
| Omega-3 Supplements | Moderate | Medium | Long-term | Fishy aftertaste, indigestion | Easy |
| Milk Thistle | Moderate | Medium | Ongoing | Rare side effects (allergy) | Easy |
Q&A Section
1. Can fatty liver disease be reversed?
Yes, fatty liver disease can be reversed through weight loss, a healthy diet, regular exercise, and managing underlying conditions like diabetes and high cholesterol. Early intervention is key to preventing further liver damage.
2. Is fatty liver disease dangerous?
If left untreated, fatty liver disease can progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cirrhosis, and eventually liver failure. However, with lifestyle changes, the disease can often be managed or even reversed.
3. What foods should I avoid if I have fatty liver disease?
Avoid high-fat, high-sugar foods like fried snacks, fast food, sugary drinks, and processed meats. Focus on whole, nutrient-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
4. How long does it take to reverse fatty liver disease?
The time it takes to reverse fatty liver disease depends on the individual and the severity of the condition. In general, significant improvements can be seen within a few months to a year of consistent lifestyle changes.
5. Do I need medication to treat fatty liver disease?
Medication is not always necessary for treating fatty liver disease. In many cases, lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise are sufficient to manage the condition. However, in more severe cases, medications may be prescribed.
Conclusion
Fatty liver disease is a manageable condition with the right lifestyle changes and medical interventions. By focusing on weight loss, a balanced diet, and regular exercise, you can significantly improve liver health. If needed, consult a healthcare provider for further guidance on medications or supplements to support liver function.
Sources
This guide offers an in-depth look at the causes, symptoms, and treatments for fatty liver disease, providing practical advice and resources for those seeking to manage or reverse the condition.






Recent Comments